Last blogpost provided a brief insight into the powerful jargons of modern electric utility industry. This week’s post aims to break down to fine detail how data science and analytics can change the electric utility at every level.
A traditional approach to studying the power system divides the system into three main categories namely generation, transmission, and distribution. We will use the same approach in this blog post to discuss the data science solution in respect to each category.
Data Science for Generation
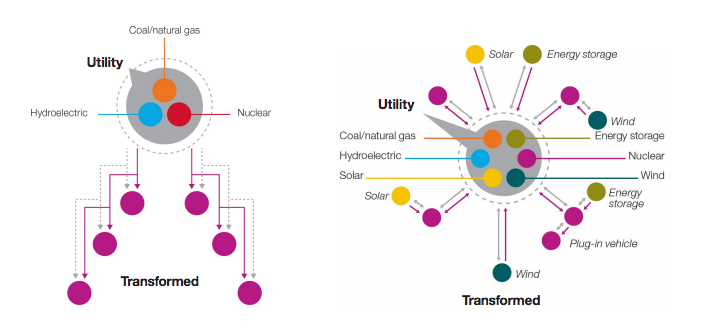
Power generation is one of most complex and expensive processes in the electrical utility industry. The power generators are required to make an educated forecast to optimize the levels at which their generators should be operating. Most of the time, the power generators own a mix of generation based on fuel sources like coal, hydroelectricity] , nuclear energy, renewable energy(wind, solar, etc.) and it is very critical to schedule these resources according to the forecasted demand for load. This classic problem is called economic dispatch and unit commitment for generation.
In addition, power plant optimization can aid in helping emissions reductions thereby saving a lot of green, both in terms of money and environment. One of the growing challenges of the modern smart grid is the implementation of distributed generation and renewable energy mix. Distributed generation (DG) refers to power generation at the point of consumption. Generating power on-site, rather than centrally, eliminates the cost, complexity, interdependencies, and inefficiencies associated with transmission and distribution. [1] This will eliminate the stress on centrally operated power plants and puts onus on local generation to be consumed at the customer’s location.
Data Science for Transmission and Distribution
Utility companies need to analyze all information about an asset including data history, maintenance records, and operating condition data to improve operations and maintenance. Insights into operations can help utilities shift away from costly time-based asset management and develop a more informed reliability-based approach of making repairs when they are actually needed. It provides a 360-degree view of assets from the individual transformer level to the entire grid, including health and risk scores, so utilities can avoid catastrophic failure by identifying the risk, impact and confidence of each asset. The combination of data integration and visualization with advanced analytics enables better decision-making and prioritization regarding maintenance, repairs and utilization. This solution can reduce operational costs and improve efficiencies by (1) reducing asset failures, (2) increasing asset utilization rates, (3) optimizing network availability, and (4) decreasing loss of service. [2]
Usage of predictive analytics along with data retrieved through smart asset management devices on the network is fast-emerging as a theme of great importance. In the near future, asset intensive utility organizations will be forced to adopt the use of predictive analytics tools/techniques to predict various dimensions of asset management using the real-time data retrieved from smart devices.[3]
Next Post: Data Science Solutions for Residential Energy Market: An Overview
Source: